SAP provides support to customers over remote connections. SAP offers worldwide 24x7 support availability: around the clock, SAP experts are at hand to provide valuable advice and assistance through remote connections to customer systems.
Additionally, every customer has full access to a wide range of SAP service products (such as the EarlyWatch Service) over established remote connections.
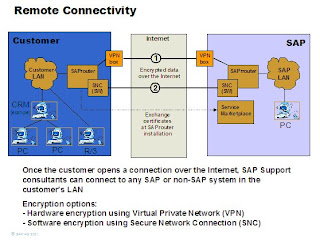
Currently, SAP offers two alternative ways to connect to the Support Network over the Internet:
1) SAProuter with Secure Network Communications (SNC) over the Internet
a. SNC secured SAProuter – SAProuter connections are established between SAP and the customer’s SAProuter to provide data confidentiality and integrity services. State-of-the-art encryption, authentication, and access control technology will be employed. No additional hardware compared to a leased-line setup is required at either end of the connection.
b. Customers are required to install a SAProuter with an official, static IP address (DHCP Addresses will not work) running SNC inbound and outbound connection to SAP at their end of the connection in a Demilitarized Zone. This SAProuter must be accessible from the Internet. All service connections between SAP and the customer must be made over the respective SAProuters.
c. Certificates needed are available on the SAP Service Marketplace.
2. Internet Virtual Private Network (VPN)

a) SNC secured SAProuter – SAProuter connections are established between SAP and the customer’s SAProuter to provide data confidentiality and integrity services. State-of-the-art encryption, authentication, and access control technology will be employed. No additional hardware compared to a leased-line setup is required at either end of the connection.
b) Customers are required to install a SAProuter with an official, static IP address (DHCP Addresses will not work) running SNC inbound and outbound connection to SAP at their end of the connection in a Demilitarized Zone. This SAProuter must be accessible from the Internet. All service connections between SAP and the customer must be made over the respective SAProuters.
c) Certificates needed are available on the SAP Service Marketplace.
 d) LAN-to-LAN IPSec VPNs are established between SAP and the customer’s network to provide data confidentiality and integrity services. These VPNs complement the leased lines in the current Remote Customer Support Network environment. State-of-the-art encryption, authentication, and access control technology will be employed. VPN equipment is required at both ends of the connection. The VPN switch at customer’s side must be reachable from the Internet.
d) LAN-to-LAN IPSec VPNs are established between SAP and the customer’s network to provide data confidentiality and integrity services. These VPNs complement the leased lines in the current Remote Customer Support Network environment. State-of-the-art encryption, authentication, and access control technology will be employed. VPN equipment is required at both ends of the connection. The VPN switch at customer’s side must be reachable from the Internet.
e) Besides the VPN equipment (also called VPN switch or VPN gateway), customers are also required to install a SAProuter with an official IP address at their end of the connection. All service connections between SAP and the customer must be made over the respective SAProuters.
f) Authentication at the VPN gateways will be regulated using static keys. SAP will generate these keys and provide them to the customer. In future, certificate-based authentication is likely to be utilized.
g) VPN access can also be achieved through a telecommunications provider. The provider will then be connected to SAP’s VPN switch, and the provider can offer connections to customers over the Internet. SAP has a list of VPN-enabled providers.
The Abstract Contents highlighting its reusability in current Scenario

Conclusion:Internet link with static IP-Address for Saprouter at customer end is required for SNC connection. This is not supported in dail-up connections. Thus normal dial-up connection is not a solution to the problem.


